|
On molecular physics and thermodynamics
Statistical and thermodynamics methods.
Molecular physics and thermodynamics - the physical science that study
macroscopic processes in bodies, due to the huge number of bodies
contained in atoms and molecules.
Molecular physics is a branch of physics that studies the structure
and properties of matter, based on the so-called molecular-kinetic
concepts. According to these ideas:
1. Any body - solid, liquid or gas is made up of a large number of very small particles of isolated molecules.
2. The molecules of any substance is in an endless chaotic motion (eg, Brownian motion).
3. Used an idealized model of an ideal gas, which provides:
a). Own volume of the gas molecules is negligible compared to the volume of the vessel (vacuum).
b). No forces between the molecules interact.
a.) Clash of the gas molecules with each other and with the walls of the vessel is elastic.
4. The macroscopic properties of bodies (pressure, temperature, etc.)
are described by statistical methods, the basic concept of which is the
statistical ensemble, ie describes the behavior of a large number of
particles through introduction of the average characteristics (average
speed, energy) the whole ensemble, and not a single particle.
Thermodynamics in contrast to the molecular-kinetic theory studies the
properties of macroscopic bodies, is not interested in their
macroscopic picture.
Thermodynamics - the branch of physics that studies the general
properties of macroscopic systems in thermal equilibrium, and the
transition between these states.
At the heart of thermodynamics are three fundamental laws, called
thermodynamics, established by summarizing a large set of experimental
facts.
Molecular-kinetic theory and thermodynamics complement each other to
form a whole, but to distinguish different methods of investigation.
Thermodynamic system - a set of macroscopic bodies that interact and
exchange energy between themselves and with other bodies. State of the
system is given by the thermodynamic parameters - a set of physical
quantities characterizing the properties of a thermodynamic system,
usually in a position to choose the parameters as temperature, pressure
and specific volume.
Temperature - a physical quantity that characterizes the state of thermodynamic equilibrium macroscopic system.
[T] = K - thermodynamic scale, [t] = ° C - International Practical
Scale. Relationship thermodynamic and international practical
temperatures: T = t + 273, for example, at t = 20 ° C, T = 293 K.
Specific volume - this volume per unit mass. When the body is homogeneous, ie ρ = const, then the macroscopic properties of a homogeneous body can represent the body volume V.
Molecular-kinetic theory (MKT) for ideal gases
§1 Law of the of ideal gases
In molecular - kinetic theory uses an idealized model of an ideal gas.
Ideal gas called gas whose molecules do not interact with each other at a distance and have a negligible own sizes.
In real gas molecules have the force of intermolecular interaction. However, H2, He, O2, N2 with n. c. (T = 273 K, P = 1.01 x 103 Pa) can be roughly considered as an ideal gas.
The process by which one of the parameters (p, V, T, S) remain constant, called isoprocesses.
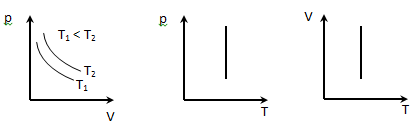
1. Isothermal process T = const, m = const, described by Boyle's law:
pV = const
2. Isobaric process p = const is described by Gay-Lussac
V = V0 (1 + α t);
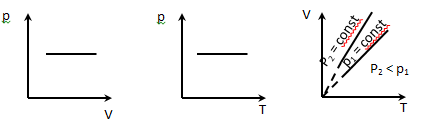
V = V0α T
α-thermal coefficient of volumetric expansion α = 1/273 K-1
3. Isochoric process V = const
Is described by Charles law
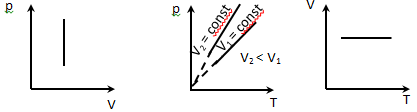
p = p0 (1 + α t);
p = p0α T
α - characterizes the dependence of the temperature. α is equal to the relative change in
volume of a gas when heated at 1 K. The experience, α is the same for all gases and is α = 1/273 K-1.
4. Mole of substance. Avogadro's number. Avogadro's law.
Atomic mass (Ar) of a chemical element is the ratio of the mass of an atom of this element to 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon isotope C12
Ar = CINT (A) (A in the periodic table)
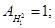 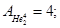 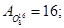 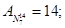 etc. etc.
Molecular mass (Mr) is the ratio of the mass of the substance molecules of the substance to 1/12 of the mass of an atom of carbon isotope C12: MH2 = 2; M02 = 32; MN2 = 28; Mair = 29; MHe = 4; MCO2 = 44.
The unit of mass equal to 1/12 of the mass of the atom C is the atomic mass unit (amu) m = 1 amu = 1.66 ·10-27 kg
The amount of substance that contains the number of particles (atoms
or molecules) equal to the number of atoms in 12 grams (0.012 kg) of
carbon called mole.
The number of particles contained in the mole of matter is called Avogadro's number.
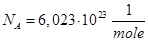
Mass of a mole is called molar mass μ. Molar mass equal ratio of the mass to the number of moles ν, which it contains
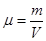
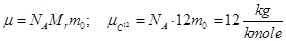
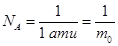
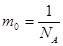
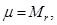 but Mr - dimensionless quantity, but Mr - dimensionless quantity, 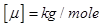 . .
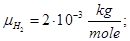 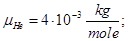 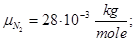  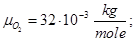 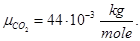
Avogadro's law: moles of any gas at normal conditions (T = 273 K, p = 1.01 • 105 Pa) took the same volume equal 22.41 ·10-3 m3/mole.
| 

