main
To the list of lectures
|
ELECTROMAGNETISM Mrot, pm, the lines of force Permanent magnets
have been known 2000 years ago, but only in 1820, H. Oersted (Danish
physicist) found that around a conductor with a current creates a
magnetic field, which affects the magnetic needle. Later, it was found
that the magnetic field is produced by moving bodies, or any charges.
The magnetic field, like the electric, is a type of matter. The
magnetic field has energy. By means of the magnetic field the
interaction between electric currents moving charges. Experience has
shown that the effects of the magnetic field on the current varies
depending on the shape of the conductor, in which the current flows, the
location of the conductor and the direction of the current. Therefore,
in order to characterize the magnetic field, it is necessary to
consider the effect on a certain current.
Direction Because current loop experiences orienting action of the field, then it in a magnetic field exerts a force couple. Rotating moment forces depends on the properties of the field at a given point and the properties of current loop
The unit of measurement of magnetic induction – Tesla
If at a given point of the magnetic field to make a variety of current loop with the magnetic moments of p1, p2, ... pn, then the torque will be different for each current loop M1, M2, ... Mn, but the ratio
for all current loops is the same and can serve to characterize the magnetic field. Magnetic induction The direction of vector A magnetic field conveniently represented with lines of force of vector determined by the right-hand rule. For linear conductor: thumb in the direction of the current, bent four fingers indicate the direction of the field line. For a circular coil with a current: four fingers - on the current direction, the thumb indicates the direction of the field line in the center of the coil. Lines of magnetic inductionbegin on positive charges and end on negative, approach perpendicular to the surface charge density of the lines of force characterizes the field.) In some cases, along with the vector
µ0 –magnetic constant ; µ - magnetic permeability of the medium - shows how many times the magnetic field in the medium more (or less) of the magnetic field in the vacuum .
where B - the magnetic field in the material, B0 - external magnetizing field. From a comparison of the characteristics of the electric field vector (vector Analogue of the electric displacement
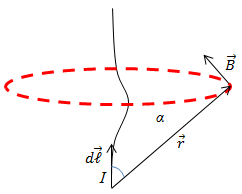
§ 2 he Biot-Savart-Laplace’s Law
Magnetic induction
Because in the Biot-Savart-Laplace law there is a vector product must be perpendicular to the plane of the vectors Modulus (magnitude) of the vector
where α –the angle between the 2.The principle of superposition of fields:
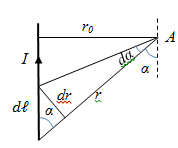
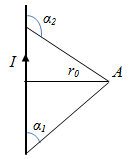
3. Application of the Biot-Savart-Laplace’s law to the calculation of magnetic fields. a) A magnetic field of the direct current
Since the
induction created by different elementary sections, which we have
broken conductor at this point have the same direction, we can sum the
geometric vectors
In the case of an infinitely long conductor
α = 90°; sin α = 1.
|

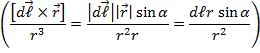
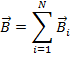
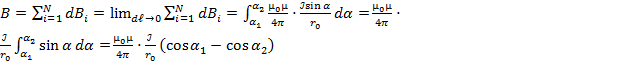
 b)
b)