| № |
Condition |
free/or 0.5$ |
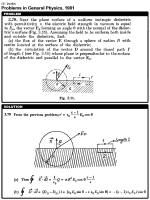
| 721 | A conductor of arbitrary shape, carrying a charge q, is surrounded with uniform dielectric of permittivity ε (Fig. 3.9). Find the total bound charges at the inner and outer surfaces of the dielectric. |
|
| 722 | A uniform isotropic dielectric is shaped as a spherical layer with radii a and b. Draw the approximate plots of the electric field strength E and the potential φ vs the distance r from the centre of the layer if the dielectric has a certain positive extraneous charge distributed uniformly: (a) over the internal surface of the layer; (b) over the volume of the layer. |
|
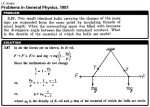
| 723 | Near the point A (Fig. 3.10) lying on the boundary between glass and vacuum the electric field strength in vacuum is equal to E0 = 10.0 V/m, the angle between the vector E0 and the normal n of the boundary line being equal to α0 = 30°. Find the field strength E in glass near the point A, the angle α between the vector E and n, as well as the surface density of the bound charges at the point A. |
|
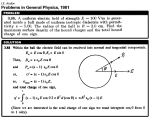
| 724 | Near the plane surface of a uniform isotropic dielectric with permittivity ε the electric field strength in vacuum is equal to E0, the vector E0 forming an angle θ with the normal of the dielectric's surface (Fig. 3.11). Assuming the field to be uniform both inside and outside the dielectric, find: (a) the flux of the vector E through a sphere of radius R with centre located at the surface of the dielectric; (b) the circulation of the vector D around the closed path Γ of length l (see Fig. 3.11) whose plane is perpendicular to the surface of the dielectric and parallel to the vector E0. |
|
| 725 | An infinite plane of uniform dielectric with permittivity ε is uniformly charged with extraneous charge of space density ρ. The thickness of the plate is equal to 2d. Find: (a) the magnitude of the electric field strength and the potential as functions of distance l from the middle point of the plane (where the potential is assumed to be equal to zero); having chosen the x coordinate axis perpendicular to the plate, draw the approximate plots of the projection Ex(x) of the vector E and the potential φ(x); (b) the surface and space densities of the bound charge. |
|
| 726 | Extraneous charges are uniformly distributed with space density ρ > 0 over a ball of radius R made of uniform isotropic dielectric with permittivity ε. Find: (a) the magnitude of the electric field strength as a function of distance r from the centre of the ball; draw the approximate plots E(r) and φ(r); (b) the space and surface densities of the bound charges. |
|
| 727 | A round dielectric disc of radius R and thickness d is statically polarized so that it gains the uniform polarization P, with the vector P lying in the plane of the disc. Find the strength E of the electric field at the centre of the disc if d << R. |
|
| 728 | Under certain conditions the polarization of an infinite uncharged dielectric plate takes the form P = P0(1 - x2/d2), where P0 is a vector perpendicular to the plate, x is the distance from the middle of the plate, d is its half-thickness. Find the strength E of the electric field inside the plate and the potential difference between its surfaces. |
|
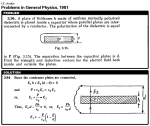
| 729 | Initially the space between the plates of the capacitor is filled with air, and the field strength in the gap is equal to E0. Then half the gap is filled with uniform isotropic dielectric with permittivity ε as shown in Fig. 3.12. Find the moduli of the vectors E and D in both parts of the gap (1 and 2) if the introduction of the dielectric (a) does not change the voltage across the plates; (b) leaves the charges at the plates constant. |
|
| 730 | Solve the foregoing problem for the case when half the gap is filled with the dielectric in the way shown in Fig. 3.13. |
|
| 731 | Half the space between two concentric electrodes of a spherical capacitor is filled, as shown in Fig. 3.14, with uniform isotropic dielectric with permittivity e. The charge of the capacitor is q. Find the magnitude of the electric field strength between the electrodes as a function of distance r from the curvature centre of the electrodes. |
|
| 732 | Two small identical balls carrying the charges of the same sign are suspended from the same point by insulating threads of equal length. When the surrounding space was filled with kerosene the divergence angle between the threads remained constant. What is the density of the material of which the balls are made? |
|
| 733 | A uniform electric field of strength E = 100 V/m is generated inside a ball made of uniform isotropic dielectric with permittivity e = 5.00. The radius of the ball is R = 3.0 cm. Find the maximum surface density of the bound charges and the total bound charge of one sign. |
|
| 734 | A point charge q is located in vacuum at a distance l from the plane surface of a uniform isotropic dielectric filling up all the half-space. The permittivity of the dielectric equals ε. Find: (a) the surface density of the bound charges as a function of distance r from the point charge q; analyse the obtained result at l → 0; (b) the total bound charge on the surface of the dielectric. |
|
| 735 | Making use of the formulation and the solution of the foregoing problem, find the magnitude of the force exerted by the charges bound on the surface of the dielectric on the point charge q. |
|
| 736 | A point charge q is located on the plane dividing vacuum and infinite uniform isotropic dielectric with permittivity ε. Find the moduli of the vectors D and E as well as the potential φ as functions of distance r from the charge q. |
|
| 737 | A small conducting ball carrying a charge q is located in a uniform isotropic dielectric with permittivity a at a distance L from an infinite boundary plane between the dielectric and vacuum. Find the surface density of the bound charges on the boundary plane as a function of distance r from the ball. Analyse the obtained result for L->0. |
|
| 738 | A half-space filled with uniform isotropic dielectric with permittivity ε has the conducting boundary plane. Inside the dielectric, at a distance l from this plane, there is a small metal ball possessing a charge q. Find the surface density of the bound charges at the boundary plane as a function of distance r from the ball. |
|
| 739 | A plate of thickness h made of uniform statically polarized dielectric is placed inside a capacitor whose parallel plates are interconnected by a conductor. The polarization of the dielectric is equal to P (Fig. 3.15). The separation between the capacitor plates is d. Find the strength and induction vectors for the electric field both inside and outside the plates. |
|
| 740 | A long round dielectric cylinder is polarized so that the vector P = αr, where α is a positive constant and r is the distance from the axis. Find the space density ρ' of bound charges as a function of distance r from the axis. |
|